Nowadays digital identity is a requirement not a choice, it has become a basic need. Digital identity management is important for verifying, providing access and securing statistical integrity and security. From online shopping to health care, from background checks of job prospects to improved performance of government services, digital identity is the foundation we build trust and efficiency into our digital lives. As we enter into the complex world of the digital age, governments, private entities, and individuals must work together to develop secure, easy to use, and at the same time innovative solutions for identity management.
Let us look at how digital identity is transforming global sectors and why it has great value in bringing about large scale change.
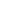
Digital Identity in Government’s Sector
Governments all over the world are adopting digital identity solutions which in turn they use to improve public services, increase transparency, and reduce fraud. Here are some of the key applications:
1. Access to Services Made Easy
Digital identities give citizens access to key services such as health care, education, social security benefits, and tax filing easily. For instance:
Estonia — e-Residency and Digital ID: Estonia is a leader in the world of digital identity. Their e-Residency program which is available to non-Estonians enables them to use Estonian business services from any part of the world. Also they have a national digital ID which is used by citizens to access a range of government services which includes voting, signing docs, and also use of online services in a secure way.
India — Aadhaar: In India Aadhaar system is the largest in the world when it comes to biometric-based digital identity. This system issues out 12 digit ID numbers which are tied to a person’s fingerprint and iris data. It also provides for easy access to services like banking, government and also subsidies.
Singapore — SingPass: SingPass in Singapore is an integrated digital identity platform which gives citizens access to government and health care services as well as financial institutions. Also it uses biometrics for identification which in turn makes the system more secure and protects users from cyber threats.
Sweden — BankID: In Sweden BankID is a very popular digital identity solution which is used all over the world. This service which we have adopted into our everyday use provides secure access to your bank, online shopping and also government services. Over 8 million Swedish users aged 15 and over use this service for their online transactions.
Canada — Verify.Me: Verify.Me in Canada is a digital identity solution which uses blockchain technology for secure and private financial transactions. We have a solution which allows users to verify their identity when working with many different organizations at the same time which in turn does not require them to share out sensitive info.
2. Prevention of Fraud and Security
By putting in place strong digital identity systems governments are able to fight off identity theft, electoral fraud and other forms of cybercrime. Also with digital IDs which are verified we see that only the identified individuals which are authorized can take part in very important processes like voting or applying for passports.
3. Intelligent Cities and Governance
Digital identity is at the core of smart city projects which see data driven solutions improve urban living. For example residents may use their digital IDs to pay for utilities, book public transport, or report issues related to the city all via one platform.
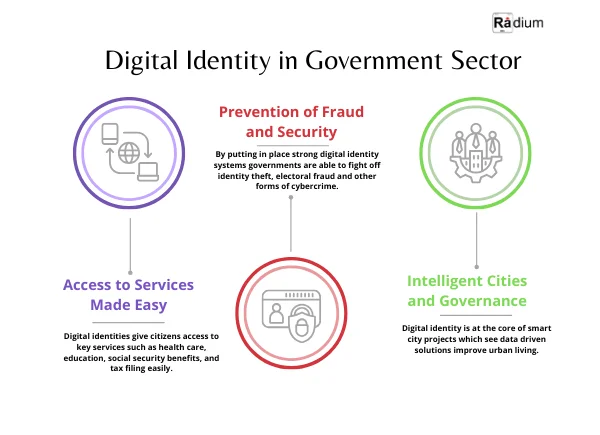
Private Sector Adoption of Digital Identity
The private sector is also into digital identity which in turn we see playing out into more personal, efficient, and secure customer experiences. In terms of which areas we are seeing this play out in:
1. Safe Online Payments
Ecommerce sites, banks, and fintech companies report heavy use of digital identity verification which we see in the prevention of unauthorized access and financial fraud. We are to see technologies like multi factor authentication (MFA), biometrics, and blockchain in use which at the same time we also see a concern for user convenience.
2. Recruiting and Employee Onboarding
Recruiting organizations and employers use digital identity tools to check out candidate credentials, perform background checks, and bring in new employees remotely. This also puts forward a faster hiring process which in turn reduces the risk of hiring unqualified people.
3. Tailored Customer Experiences
Retailers and service providers use digital identities to present targeted recommendations which match user preferences and see to it that behavior patterns of the users are taken into account. By walking the line between personalization and privacy protection businesses are able to develop stronger relationships with their customers.
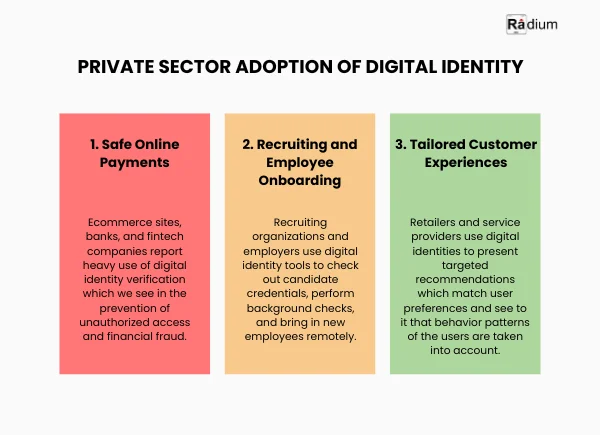
Global Impact of Digital Identity
Digital identity is transforming beyond our individual nations and industries, we see it play out on the global stage which in turn is presenting solutions to global issues and bringing about international cooperation.
1. Financial Access
For that which is of the order of the unserved in development we have digital identity as the entry point to formal finance. In Kenya’s M-Pesa we see digital IDs play a key role in secure payment, savings and loan facilities for which traditional banking is not a requirement.
2. Support for Refugees and Humanitarian Aid
Digital identity programs are a great asset in humanitarian work. Many refugees do not have physical documentation but via the digital IDs which UNHCR issues they are able to access aid, health care and education.
3. Cross Border Cooperation
Countries are at the table as they develop digital identity systems which in turn will improve cross border trade, travel and communication. In the case of the European Union we see the eIDAS regulation which is a step toward standardizing electronic identification and trust services across member states.
Biometric authentication: Fingerprint scans, face recognition, and Iris scans.
Blockchain: Decentralized identity solutions improve privacy and reduce data violations.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Identity verification powered by AI improves fraud detection and risk assessment.
Convenience and user experience: Digital identity improves and simplifies a lot in digital space what we do as individuals. Biometric technology in digital identity gets rid of the requirement of remembering many usernames and passwords that, in turn, facilitate access to devices, authenticate transactions and use services.
Greater accessibility and inclusion: digital identification that has seen an increase in the use of this term is that it accesses more people to basic services that include financial, health and educational. It is also very much for people in remote and needy areas that, in turn, help close the digital gap.
Allowing global mobility and perfect trips: Digital wallets that have digital passports, departure passes and other travel credentials that we see as a great convenience for travelers. They provide a fast and safe biometric check at airports, hotels and border crossings, which in turn improves travel experience and reduces friction on international travel.
Supporting smart cities and sustainable life: Digital presence personally and on -line, which we call digital identities, improve access to a wide range of city services, improve quality of life, and we also see that in the city, large -scale sustainability is improved. For example, citizens can use their digital ID to reserve a place in the sports complex, access on -line library features, or control smart smart domestic devices.
While we see the value in digital identity which is great, we also see issues that come with wide scale adoption which must be carefully addressed:.
1. Privacy Issues
Collect issues of private data collection and storage which in turn fosters overreach and surveillance. Governments and organizations are to improve in terms of transparency, consent, and also in what we put out in terms of data collection to restore public trust.
2. Cyber risks
As technology plays a larger role in our day to day lives we also see that digital identities are what hackers target the most. Which is why it is key to use robust encryption, perform regular audits, and stay ahead of threats.
3. Gap between digital haves and have nots
Not all of us have the same access to technology and the internet. We can bridge this gap with inclusive policies and development of affordable infrastructure which leaves no one out.
To overcome these, stakeholders must collaborate: To that end stakeholders must work together:
Governments must put in place clear rules and also put forward large scale infrastructure projects.
Private Enterprises should adopt state of the art technologies and focus on user centered design.
People should be made aware of safe digital practices which include using strong passwords and to recognize phishing.
Digital transformation projects’ success is in how we do identity management, protection, and use of digital identities. Through investment in the latest tech, compliance with regulation, and education of users in privacy best practices we open up to great innovation.
Imagine a future where: Envision a world where:
Citizens use government digital services which are secure.
Businesses which cross borders do so with the use of universal IDs.
Individuals have full right over their personal data which includes who may access it and for what purpose.
This vision is at hand but to achieve it requires action from all stakeholders. We may build a safer, smarter and more inclusive digital environment which is enabled by trust in digital identities.
By integrating robust digital identity frameworks with effective management practices, we can enhance security, improve user experiences, and foster trust in digital interactions. Digital identity we see as a far greater thing than just a tech play; it is the foundation of what we have built today. It extends into government, into business, and out to communities which all over the world are using it to address our biggest issues. As we push into this new way of doing things let us also put forth that we do so in a spirit of collaboration, inclusivity, and resilience in the digital age.
What measures will you put in place for digital identity? Tell us your ideas!
Stay with us as we report on the issue of digital identity which is in a state of change.
For more understanding, you can check out our Digital Identity Management article.
Incorporating modern technologies with the government operations is referred to as digital transformation in the government sector. Digital transformation enhances accessibility, efficiency, employee performance and most as citizen engagement, responsiveness and overall satisfaction. Government services are enhanced by the use of cloud computing, data analytics, and mobile technologies.
Digital transformation in government allows for streamlined processes, reduced paperwork, and automation of repetitive tasks.
Digital Identity can lead to identity theft, data leaks, and worries about privacy due to too much data collection and wrong use. Stealing digital identities might put people at risk in many ways.
A digital ID has several upsides. It lets people use online services, like their bank account, and prove who they are without risking personal info such as a password getting into the wrong hands.
Digital identity will keep playing a key role in safeguarding data and resources in the years to come. We're seeing more teamwork and support for digital identity these days.
Aadhaar stands as the biggest biometric ID system . By May 2023 almost all adults in India had Aadhaar IDs. World Bank Chief Economist Paul Romer called Aadhaar "the most advanced ID program in the world.