In our present global environment which is so connected, national security goes beyond physical frontiers and military power. Digital security is of equal importance in that it protects citizens from cyber attacks which we see in the case of India which has put in place of advanced solutions like L1 security for biometric authentication. Today in this blog we will look at how traditional and digital security play together. We also look at India’s great steps in improving its cyber security framework which includes the move to more secure L1 biometric devices to protect citizens’ data during KYC processes and financial transactions.
Protection against financial fraud and identity theft
Rapid increase in digital payment transactions has seen a 400% growth in large scale cyber fraud cases in India during FY 2024 which in turn has caused $20 million in losses; we need digital protection measures to put a stop to such issues.
Defense from spam, phishing and malware
As we connect more we increase our risk of theft, fraud and abuse. It is of great importance that we see to it that our cybersecurity and law enforcement agencies work in tandem to deal with issues like spear phishing, social media scams and other online threats.
Securing critical infrastructure and digital identities
A secure, stable, and resilient cyber space which forms the base of our national security in issues like elections and power grids -- also as a result of proactive system hardening and incident response.
Maintaining privacy and data integrity
Data protection frameworks see to it that consumers’ private info is protected from theft, damage, or loss which in turn results in a more widespread use of digital services.
Enabling economic growth through trust in digital tools
As markets move online we see that strong cyber security measures in fact do the work of encouraging investment and competition by telling businesses and consumers that their transactions and innovations are in a secure environment.
Upholding digital sovereignty
Control of national data flow and infrastructure that includes cloud servers and telecommunication is key to a country in protecting its citizens’ info and from external manipulation.
The Dual Nature of National Security
Traditional Security Framework
Border Security and Armed Forces: Traditionally a nation’s security has been determined by the power of its military and the defense of its geographical borders against foreign threats.
Visible Defense Mechanisms: These include physical assets like military personnel, weapons systems, and physical barriers which protect territorial integrity.
Geopolitical Dimensions: This type of security we see to include issues of conventional war and also the maintenance of a balance of power through the use of physical presence and deterrence.
Resource Allocation: Large parts of the national budget go to defense which is in support of ready response to external aggression and protection of sovereignty.
Invisible Frontiers: Unlike physical perimeters, digital boundaries are flexible and in a constant state of change which in turn requires we use different protective strategies than what we see in traditional security.
Critical Infrastructure Protection: Digital security protects critical national infrastructure which includes power grids, transportation systems, and communication networks from cyber attacks.
Economic Stability: Cy info systems which put in place to avoid large scale economic disruption that may result from great data breaches or digital infrastructure attacks.
Citizen Data Protection: Governments are to put in place strong digital security measures which protect citizens’ personal information in government databases from unauthorized access.
Financial Frauds and Scams
Massive Financial Losses: India saw reported losses of about $1.5 billion to cyber fraud which occurred in the first nine months of 2024 thus which is a large scale issue of poor digital security.
Stock Trading Scams: In the past report of cyber crimes in India these were the largest reported issue, we saw reports of 4,636 crores from 2,28,094 cases.
Investment Frauds: In the second place which is in terms of damage was reported to be of ₹3,216 crore from over 1 lakh complaints that affected citizens’ savings and investments.
Digital Arrest Scams: This growing threat which saw the loss of 1.616 billion from around 63,481 reports of crime shows the evolution of criminal use of new fraud methods.
Data Security Compromises
Identity Theft Risk: Poor protection of personal identifiable info may result in identity theft and which in turn will affect citizens’ financial security and reputation.
Privacy Violations: Unauthorised access of personal data results in privacy violations which in turn affect individuals’ fundamental right to privacy and data protection.
National Security Implications: Government database breaches of sensitive info may put national security ops and intelligence at risk.
Cross-Border Threats: In 2024 it was reported that nearly half of the cyber fraud cases in India were from Southeast Asian countries (Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos) which also points out at the global issue of cyber security.
Scale of the Problem
Growing Complaint Volume: Since 2021 the Citizen Financial Cyber Fraud Reporting and Management System reports 30.05 lakh complaints which also see losses of 27,914 crore.
Accelerating Threat Landscape: In 2024 we saw a report of over 12 lakh cyber scam cases which is a large-scale issue of digital security.
International Criminal Networks: In over 45% of cases of cyber fraud reported in India we see that they are from Cambodia, Myanmar and Laos, which shows the issue is international.
Diverse Attack Vectors: From schemes which invest in false promises to what some term as digital crimes, cyber criminals are always coming up with new ways to take advantage of digital system flaws and human psychology.
Cybersecurity Principles
Confidentiality: Ensuring that private data is for authorized persons only, protecting military secrets and other classified info.
Integrity: Ensuring that only approved personnel may alter data which in turn upholds the trust of digital info.
Availability: Ensuring that the systems and services we provide which are critical are available to our users as agreed at all times and do not fall out of service.
Comprehensive Protection: Effective security in the cyber domain is to protect all forms of data against theft and also loss which includes sensitive data, protected health information and intellectual property.
UIDAI's Security Enhancement Initiative: UIDAI has implemented a shift from L0 (Level 0) fingerprint Registered Devices to more secure L1 (Level 1) fingerprint Registered Devices.
Fundamental Difference in Processing: In L0 devices biometric data is encrypted on the host device post scan, in L1 devices data is encrypted at the point of capture which is the scanning device itself thus we see improved security.
Phased Implementation Approach: UIDAI has put in place a transition plan which sees the phase out of all fingerprint L0 Registered Devices by June 30, 2025, after which only fingerprint L1 Registered Devices will be accepted for Aadhaar based authentication.
Continuation of Iris Devices: Iris based systems which are of a more secure nature will continue to operate under present protocols which may not be changed at this time.
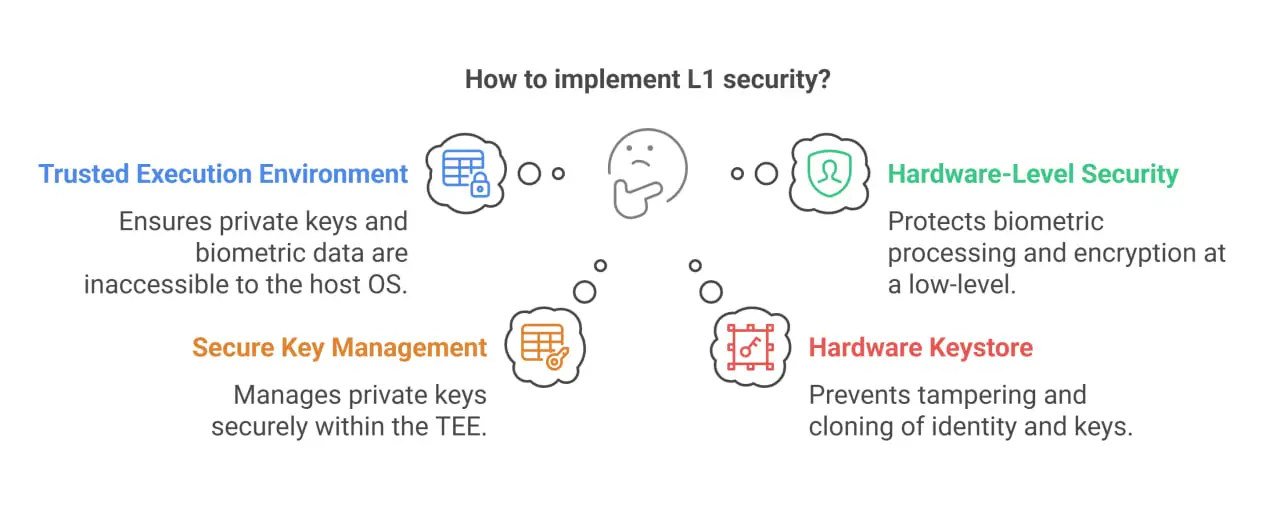
Technical Aspects of L1 Security Implementation
Trusted Execution Environment: L1 compliance requires that in a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) which the host OS processes do not have access to for private keys or biometric injection.
Hardware-Level Security: Critical to which the biometric processing and extraction, signing of bio elements, and PID block encryption are applied which must take place in the TEE at a host operating system level below.
Secure Key Management: Private keys should be handled within the TEE, for storage outside of it use TEE instance specific AES 256 bit keys.
Hardware Keystore Requirements: Identity of the chip, key pair generation, and bio element signing must take place in a hardware keystore (secure crypto block) to prevent tampering or cloning.
BIS Registration Requirement: The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has put in place a registration of optical fingerprint scanners under what is of the Compulsory Registration Scheme as per IS 13252 (Part 1):2010 which came into effect from May 23, 2018.
Certification Process: The at large first set of L1 RD devices got certified on October 30, 2022 which was a very large milestone in the establishment of a more secure authentication ecosystem.
Distinct Registration Procedures: BIS registration processes for optical fingerprint scanners vary according to if they are made within or out of the U.S. also foreign manufacturers have specific requirements.
Implementation Timeline: Authentication User Agencies (AUA) and KYC User Agencies (KUA) will put into use the new L1 RD as they roll out from the defined time frame in a bid to be compliant.
Conclusion
National security in the present time has a complex approach which includes at large traditional military and border security with also robust digital protection systems. By the example of India which reports great financial loss to cyber scams and has put in place improved L1 security for biometric devices we see that the digital frontiers is a key vulnerability which in turn requires very advanced countermeasures. The Indian government’s strategic move to improve biometric security from L0 to L1 devices is proof that they think protecting citizens’ digital identity is of the same importance as protecting physical borders. This transformation highlights the growing recognition that digital identity is foundational to national security, governance, and economic empowerment. To understand how secure identity systems shape our future and safeguard personal data in a connected world, read more on the importance of digital identity here.
The shift towards L1 biometric devices is a great step forward in the digital authentication space which in turn is very much the case for Aadhaar based transactions that make up the base of India’s digital identity structure. Through the use of hardware based security features and implementation of encryption at the time of capture India is setting new standards which in fact are a response to the complex nature of today’s cyber threats.
As we see the growth of digital technologies, the role of traditional and digital security measures in tandem becomes more so which in turn requires continuous innovation, investment, and international cooperation to see to it that we protect our nations and citizens in the physical and digital worlds.
The term security in the modern world means protecting information, systems and networks from cyber risks such as hacking, data loss, malware, and identity theft. It includes cybersecurity, data privacy, encryption, and secure digital infrastructures that protect individuals, businesses, and governments in an advanced connected world.
Technology plays a crucial role in national security for surveillance and intelligence, data security, border management, and identifying potential threats. Governments employ satellite images, AI facial recognition, biometrics, drones, and encryption to curb terrorism, cyber warfare, and lawlessness.
Digital Security is Important for Data protection, Business continuity, Compliance with regulations, Enhanced customer trust, National security, Damage reputation, Denying unwanted access, Prevention of cyber attacks, Disrupt business activity, Improved cyber posture, Phishing, Safeguarding critical infrastructure, Safeguarding online transactions, Staying strong amidst competition, System availability and improved data
Biometric data, which include fingerprints and iris scans, complements the security and reliability of Aadhaar-linked services. However, it isn't compulsory for all individuals to update their biometrics except required for specific purposes. Verify with UIDAI for current guidelines.
UIDAI has officially discontinued the use of L0 biometric devices for Aadhaar-related applications. The L0 devices will no longer be compatible with Aadhaar authentication and only be used on non-Aadhaar portals. Whereas, L1 biometric devices offer a higher level of security. Equipped with a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE), L1 device ensures secure data signing and encryption. They use advanced encryption methods and secure device identification protocols to prevent biometric records, efficiently preventing misuse or fraudulent cases. Transitioning to L1 device is important for compliance and tomaintain secure biometric operations.